Cryptography attacks are categorized as either passive or active attacks. A passive attack is usually implemented just to discover information and is much harder to detect because it is usually carried out by eavesdropping or packet sniffing. Active attacks involve an attacker actually carrying out steps, like message alteration or file modification. Cryptography is usually attacked via the key, algorithm, execution, data, or people. But most of these attacks are attempting to discover the key used.
Cryptography attacks that are discussed include the following:


QUIZ TIME * – Practicing questions along with Concepts is Best way to Maintain Interest in Study. Hence, Please take some time for a small Quiz on Cryptanalytic Attacks? – Please click on below image for quiz to start.
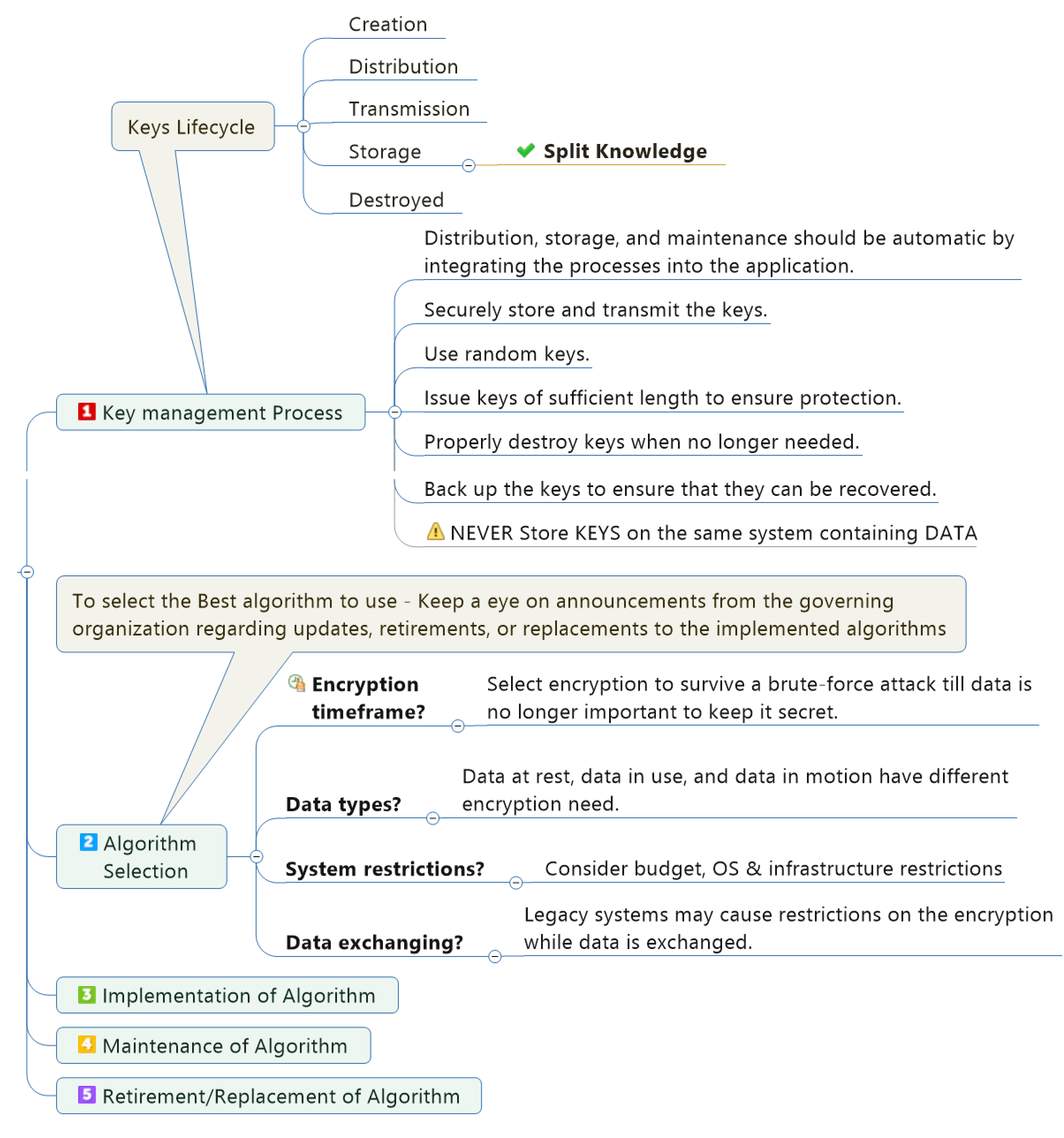
Cryptography Lifecycle
* The questions in these practice tests are listed to help you study information and concepts that are likely to be tested on CISSP certification and do not represent questions from any actual test. Your score on these practice tests is not meant to and will not correlate to any particular score on any test.
Transcript
- Cipher-text only attack
- An attacker uses several “encrypted message” to figure out the key
- Not much successful
- Known plaintext attack
- An attacker uses “Plaintext and Ciphertext” versions of a message to discover the key used
- Attacker implements
- Reverse engineering
- Frequency analysis
- Brute force
- Chosen plaintext attack
- Attacker select a Plaintext with a hope of getting Ciphertext; Then compare Plaintext and Ciphertext to get Key
- Social Engineering
- Intimidation
- Enticement
- Inducement
- Brute Force
- Requires considerable time and processing power
- Rainbow Tables
- Salting
- Differential Cryptanalysis
- Measures the execution times and power required by the cryptographic device
- The measurements help to detect the key and algorithm used
- Birthday Attack
- Collision
- Dictionary Attack
- Requires considerable time and processing power
- Replay attack
- Intercept encrypted message
- Most commonly for Authentication message
- The Best countermeasure: Timestamp, Timeouts, Sequence Numbers
- Analytic Attack
- Attackers use known “structural weaknesses or flaws” to determine the algorithm used
- Statistical Attack
- Use known statistical weaknesses of an algorithm
- Factoring Attack
- Attack is carried out against the RSA algorithm by using the solutions of factoring large numbers
- Meet-in-middle attack
- An attacker tries to break the algorithm by encrypting from one end and decrypting from the other to determine the mathematical problem used
- 2DES

It’s worth reading. I didn’t waste my time reading this.. It added to my knowledge again.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you for your valuable inputs.
LikeLike
Are considering to develop the same for other domains as well
Like Domain 4 to domain 8
LikeLiked by 1 person
Absolutely Kiran. I will be developing for other domains as well. If you have any further feedback; it is highly appreciated.
LikeLike
Pingback: Domain 3: Security Architecture and Engineering – mrcissp
Definition of Differential cryptanalysis is incorrectly stated above.
Differential cryptanalysis looks at ciphertext pairs generated by encryption of plaintext pairs with specific differences and analyzes the effect and result of those differences.
The details mentioned is of a Side Channel attack.
LikeLike